Contact 8897306498 for online classes
Online and offline classes in Hyderabad
Home tuitions in Manikonda, shaikpet, Jublee hills Hyderabad
Home tuitions in Manikonda, shaikpet, Jublee hills Hyderabad Physics and Chemistry offline and online tuitions Contact 8897306 498 on whats...
Tuesday, 31 May 2016
Important Definitions in High school Chemistry
Saturday, 28 May 2016
Answers
- Na2CO3
- MgSO4
- ZnO
- Al(OH)3
- CuSO4
- AgCl
- KNO3
- NaOH
- CaCO3
- NaHSO4
- FeS
- ZnS
- NH4Cl
- NH4NO3
- K2Cr2O7
- NaAlO2
- NiSO4
- FeCl3
- HCl
- NaCl
Practice bits - Writing Chemical formulas for class 7
Write the formulas of the following compounds:
- Sodium carbonate
- Magnesium sulphate
- Zinc oxide
- Aluminium hydroxide
- Copper(II) sulphate
- Silver(I) chloride
- Potassium nitrate
- Sodium hydroxide
- Calcium carbonate
- Sodium bisulphate
- Iron(II) sulphide
- Zinc sulphide
- Ammonium chloride
- Ammonium nitrate
- Potassium dichromate
- Sodium aluminate
- Nickel sulphate
- Iron (III) chloride
- Hydrogen chloride
- Sodium chloride
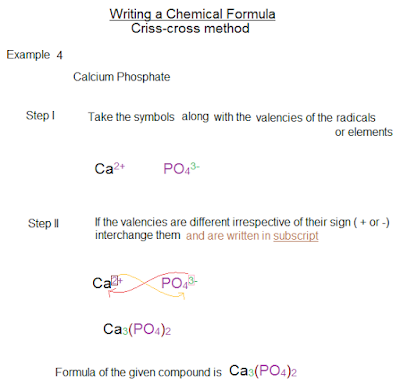
Valency chart for chemistry ICSE - ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10
Valency chart - for writing chemical formulas of chemical compounds - criss-cross method
This valency (oxidation states) chart helps in writing the molecular formula of chemical compounds
|
Positive ions/radicals |
Negative ions/radicals |
||
|
Monovalent (valency-I) |
|||
|
Potassium |
K+ |
Chloride |
Cl– |
|
Sodium |
Na+ |
Bromide |
Br– |
|
Copper(I)/
Cuprous |
Cu+ |
Iodide |
I– |
|
Mercury(I)/
Mercurous |
Hg+ |
Hydroxide |
OH– |
|
Silver(I)/
Argentous |
Ag+ |
Hydrogen
carbonate/ bi carbonate |
HCO3– |
|
Ammonium |
NH4+ |
Hydrogen
sulphite/ bi sulphite |
HSO3– |
|
Hydrogen |
H+ |
Hydrogen
sulphate/ bi sulphate |
HSO4– |
|
|
|
Nitrite |
NO2– |
|
|
|
Nitrate |
NO3– |
|
Divalent (valency-II) |
|||
|
Calcium |
Ca2+ |
Carbonate |
CO32– |
|
Magnesium |
Mg2+ |
sulphite |
SO32– |
|
Zinc |
Zn2+ |
sulphate |
SO42– |
|
Iron(II)/
ferrous |
Fe2+ |
sulphide |
S2– |
|
Lead(II)/
plumbous |
Pb2+ |
oxide |
O2– |
|
Nickel |
Ni2+ |
dichromate |
Cr2O72– |
|
Cobalt |
Co2+ |
zincate |
ZnO22– |
|
Copper(II) /cupric |
Cu2+ |
plumbite |
PbO22– |
|
Mercury(II)/
mercuric |
Hg2+ |
|
|
|
Silver(II)/
argentic |
Ag2+ |
|
|
|
Tin(II) stannous |
Sn2+ |
|
|
|
Tri valent (valency-III) |
|||
|
Aluminium |
Al3+ |
nitride |
N3– |
|
Iron(III)/
ferric |
Fe3+ |
Phosphate |
PO43– |
|
Chromium |
Cr3+ |
|
|
|
TETRA
valent(valency-IV) |
|||
|
Lead(IV)/
plumbic |
Pb4+ |
Carbide |
C4– |
|
Tin(IV) /stannic |
Sn4+ |
|
|
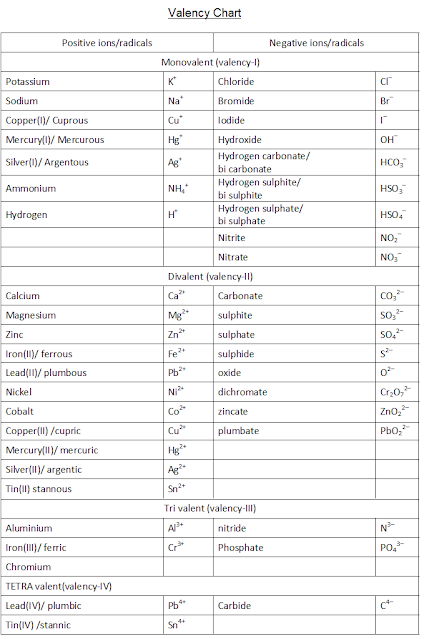 |
| valency chart for writing chemical formulas |
Chapter wise Practice Papers
- Write a Sample Online Test 25M
- ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 PRACTICE PAPERS
- ICSE PHYSICS
- ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 - Observation based questions chapter-wise
- ICSE CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY Give Reasons
- Diagrams - ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10
- ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 Percentage composition
- Empirical Formula class 10 chemistry ICSE
- ICSE CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY MODEL PAPERS
- Click here for More