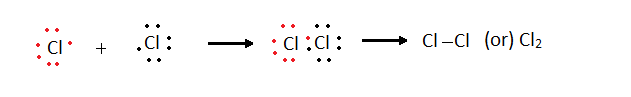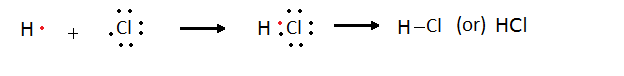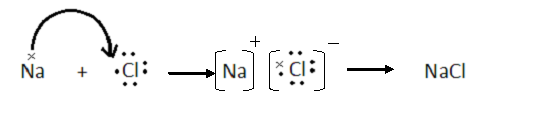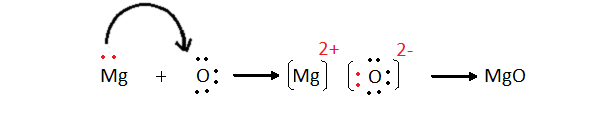Contact 8897306498 for online classes
Online and offline classes in Hyderabad
Home tuitions in Manikonda, shaikpet, Jublee hills Hyderabad
Home tuitions in Manikonda, shaikpet, Jublee hills Hyderabad Physics and Chemistry offline and online tuitions Contact 8897306 498 on whats...
Wednesday, 13 January 2021
Class 10 Practical Chemistry ICSE pdf
Class 10 Organic Chemistry notes ICSE pdf
Class 10 Organic Chemistry notes ICSE pdf
nomenclature-preparation of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, test for unsaturation
Class 10 Nitric acid ICSE notes pdf free download
Class 10 Nitric acid ICSE notes
class-10-nitric-acid-icse-notes-pdf-download-model papers-practice papers-worksheets
Class 10 Metallurgy notes ICSE pdf
Class 10 Metallurgy notes ICSE pdf
# Metallurgy notes, work sheets, model papers, practice papers
ICSE class 10 CHEMISTRY notes pdf download
Acid base and salts class 10 notes
Class 10 Acids Bases and Salts ICSE notes
Acid base and salts class 10 notes
CLASS 10 Chemical Bonding ICSE notes
CLASS 10 Chemical Bonding ICSE notes
Covalent
bond:
The bond formed by the mutual sharing of electron
pairs between the given pairs of atoms (of same or different kind) of non
metals.
Covalent compound (molecule) : The compounds
(molecules) formed as a result of mutual sharing of electrons between the atoms
are called covalent compounds.
Covalency: The number of electron pairs that an atom
shares with other atom/s to get stable electronic configuration.
Formation covalent molecules - Electron dot representation
·
The element which has 7 valence
electrons (i.e. short of one electron for octet configuration) contributes one
electron and shares one pair of electron with other atom.
Cl - 2,8,7 Cl
- 2,8,7 Chlorine molecule single covalent bond
·
The element having 6 valence electrons
(short of 2 electrons) contributes 2 electrons hence shares two pairs of
electrons.
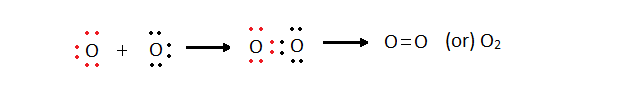
Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen molecule Double bond
2,6 2,6
·
Similarly the element with 5 valence
electrons contributes 3 electrons and shares three pairs of electrons.
Nitrogen Nitrogen Nitrogen molecule
2,5 2,5 Triple
bond
·
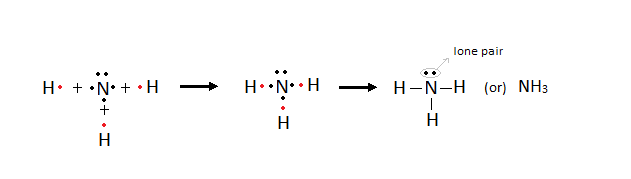
Formation of Hydrogen molecule
·
Formation of Methane molecule (CH4)
·
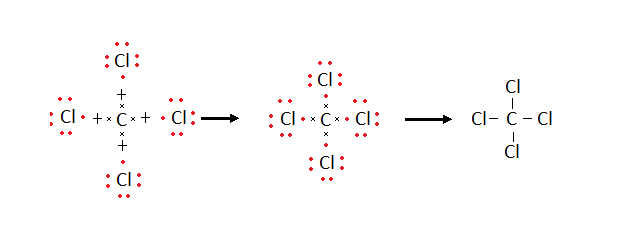
Formation of Carbon tetra chloride molecule (CCl4)
Formation of Hydrogen chloride molecules (HCl)
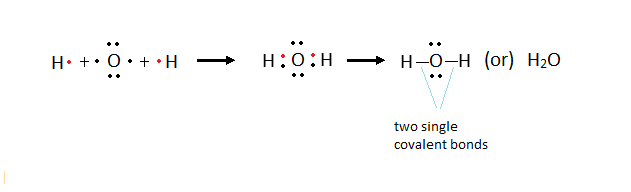
· Formation of Water molecule:
Ø Lone
pair: The pair of electrons which is not involved in any
bond formation.
for complete chapter pdf file click here class 10 Chemical Bonding pdf
Tuesday, 12 January 2021
Class 10 Chemical bonding ICSE notes
Class 10 Chemical bonding icse notes
Electrovalent bond (or) Ionic bond :
Electrovalent compound:
The compounds formed as a result of the transfer electrons.
Electrovalency:
The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom of an element to attain
stability.
The electrovalent bond is possible
between a metal and a non metal. The metal atom atom loses electron/s to
nonmetal atom so that the metal and the nonmetal attain stable electronic
configuration.
Formation of Electrovalent compounds - Electron dot representation
ü
As the metal loses electron/s it is
oxidized and forms a cation (positive ion).
Oxidation:
Na – e- -->Na+
Mg – 2e- --> Mg2+
ü The
non metal atom accepts electron/s and it is reduced to form an anion (negative
ion).
Reduction:
Cl2 + 2e- -->2Cl-
O2 + 4e- --> 2O2-
Formation
of Electrovalent (Ionic) Compounds:
Example
1 Sodium chloride ( NaCl):
Sodium
is a metal with electronic configuration 2,8,1 – has one valence electron.
Chlorine
is a non metal with electronic configuration 2,8,7 – has 7 valence electrons.
Sodium
has to lose one electron from its valence shell to attain the electronic
configuration of its nearest noble gas (Neon) i.e. 2, 8.
Chlorine
has gain one electron for the electronic configuration of its nearest noble gas
(Argon) i.e 2,8,8
Hence
Sodium loses its one electron from the valence shell to the chlorine atom.
Representation
of Sodium Chloride using electron dot structures
Example 2 Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Mg – electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2- it loses 2
electrons
O – electronic configuration is 2,6 – it has to gain
two electrons.
One Magnesium atom donates two electrons to the
Oxygen atom.
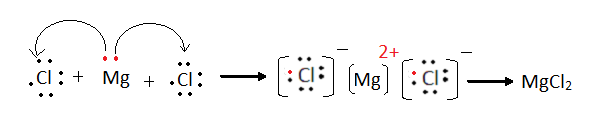
Example 3 Magnesium
Chloride (MgCl2)
Mg
– 2,8,2 – Mg atom has to lose 2
electrons and
Cl – 2,8,7 – each Chlorine atom requires one more
electron to get the stable electronic configuration.
Hence Mg
atom donates one electron to each chlorine atom.
Tuesday, 5 January 2021
ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 - ELECTROLYSIS NOTES PDF FILE
Electrolysis Notes ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 - ELECTROLYSIS NOTES PDF FILE
ICSE CHEMISTRTY CLASS 10 Notes, practice papers, chapter wise notes, chapter-wise practice papers
Friday, 1 January 2021
Why Sulphuric acid can form two types of salts?
Why Sulphuric acid can form two types of salts?
H2SO4 + NaOH --> NaHSO4 + H2O
H2SO4 + 2NaOH --> Na2SO4 + 2H2OSaturday, 7 May 2016
CLASS 10 Electrolysis notes ICSE CHEMISTRY
ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 - Electrolysis notes
CLASS 10 Electrolysis notes ICSE can be downloaded from here.
icsechemistry16 blog also provides model papers, practice papers, chapter-wise test papers etc.
Chapter wise Practice Papers
- Write a Sample Online Test 25M
- ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 PRACTICE PAPERS
- ICSE PHYSICS
- ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 - Observation based questions chapter-wise
- ICSE CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY Give Reasons
- Diagrams - ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10
- ICSE CHEMISTRY CLASS 10 Percentage composition
- Empirical Formula class 10 chemistry ICSE
- ICSE CLASS 10 CHEMISTRY MODEL PAPERS
- Click here for More