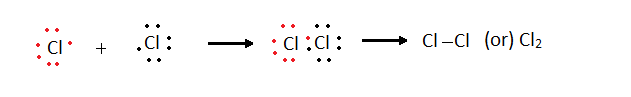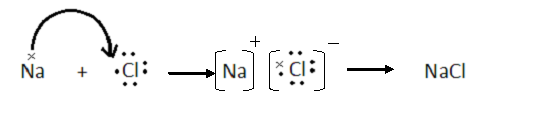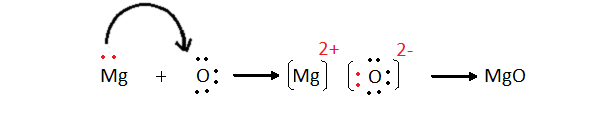Class 10 Chemical bonding icse notes
Electrovalent bond (or) Ionic bond
:
The electrostatic force of attraction which binds two or more oppositely
charged ions formed by the transfer of electron/s from the metal atom to the
non metal atom.
Electrovalent compound:
The compounds formed as a result of the transfer electrons.
Electrovalency:
The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom of an element to attain
stability.
The electrovalent bond is possible
between a metal and a non metal. The metal atom atom loses electron/s to
nonmetal atom so that the metal and the nonmetal attain stable electronic
configuration.
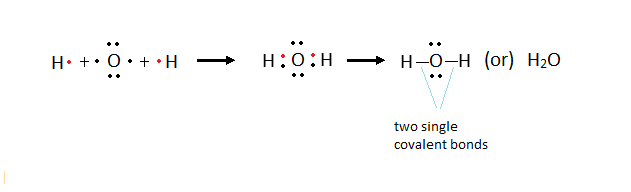
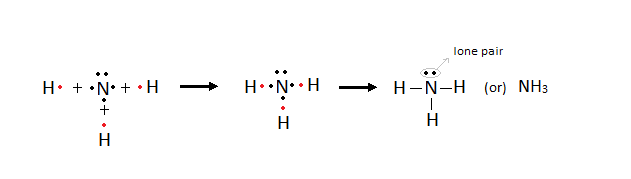
Formation of Electrovalent compounds - Electron dot representation
ü
As the metal loses electron/s it is
oxidized and forms a cation (positive ion).
Oxidation:
Na – e- -->Na+
Mg – 2e- --> Mg2+
ü The
non metal atom accepts electron/s and it is reduced to form an anion (negative
ion).
Reduction:
Cl2 + 2e- -->2Cl-
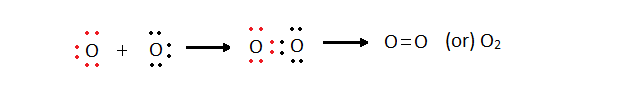
O2 + 4e- --> 2O2-
Formation
of Electrovalent (Ionic) Compounds:
Example
1 Sodium chloride ( NaCl):
Sodium
is a metal with electronic configuration 2,8,1 – has one valence electron.
Chlorine
is a non metal with electronic configuration 2,8,7 – has 7 valence electrons.
Sodium
has to lose one electron from its valence shell to attain the electronic
configuration of its nearest noble gas (Neon) i.e. 2, 8.
Chlorine
has gain one electron for the electronic configuration of its nearest noble gas
(Argon) i.e 2,8,8
Hence
Sodium loses its one electron from the valence shell to the chlorine atom.
Representation
of Sodium Chloride using electron dot structures
Example 2 Magnesium Oxide (MgO)
Mg – electronic configuration is 2, 8, 2- it loses 2
electrons
O – electronic configuration is 2,6 – it has to gain
two electrons.
One Magnesium atom donates two electrons to the
Oxygen atom.
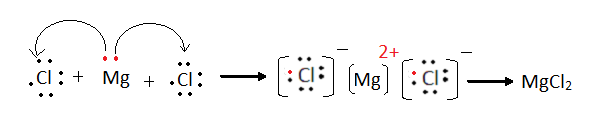
Example 3 Magnesium
Chloride (MgCl2)
Mg
– 2,8,2 – Mg atom has to lose 2
electrons and
Cl – 2,8,7 – each Chlorine atom requires one more
electron to get the stable electronic configuration.
Hence Mg
atom donates one electron to each chlorine atom.